Information Architecture: A Cornerstone of Effective Digital Experiences

What is Information Architecture?
Information architecture (IA) is the design of information spaces, often considered a bridge between people, data, and technology. In simpler terms, it’s about organizing and labeling information so that users can find what they need efficiently and effectively. Think of it as the blueprint for a digital product, guiding users through their journey.
The Business Impact of Information Architecture: A Deeper Dive
Information architecture (IA) is often seen as a technical aspect of digital product design. However, its impact on a business’s bottom line is significant and far-reaching. Let’s explore some of the key business benefits, along with the underlying reasons for each:
Increased Conversions and Revenue
Enhanced User Experience: A well-structured IA leads to a more intuitive and satisfying user experience. When users can easily find what they need, they are less likely to become frustrated and abandon their journey. This, in turn, increases the likelihood of conversion.
Reduced Cart Abandonment: A clear and organized checkout process can help reduce cart abandonment rates. When users are not confused or overwhelmed by the checkout process, they are more likely to complete their purchase.
Improved Product Discovery: Effective IA can help users discover products or services they might not have otherwise considered. By organizing information in a way that is easy to understand and navigate, businesses can expose users to a wider range of products and services, increasing the potential for sales.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty

Reduced Frustration: A poorly designed IA can lead to frustration and confusion, which can damage customer satisfaction. When users struggle to find what they need, they may become frustrated and less likely to return to the website or app.
Improved Brand Perception: A positive user experience can enhance a brand’s reputation and increase customer loyalty. When users have a positive experience, they are more likely to associate the brand with quality and reliability.
Increased Customer Lifetime Value: Satisfied customers are more likely to return and make repeat purchases, increasing their lifetime value to the business. By providing a positive user experience, businesses can cultivate a loyal customer base that generates recurring revenue.
Improved Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Better Crawlability: Search engines value well-organized content. A well-structured IA can improve a website’s crawlability, making it easier for search engines to index and understand. This can lead to higher search engine rankings and more organic traffic.
Improved User Engagement: When users can easily find what they need, they are more likely to stay on a website longer. This can improve a website’s bounce rate and time on site, which are important SEO factors.
Targeted Content: A well-organized IA can help ensure that content is targeted to the right audience, improving its relevance and effectiveness. When content is well-organized and easy to find, it is more likely to be relevant to the user’s search query, which can improve its search engine ranking.
Reduced Development and Maintenance Costs
Preventive Design: A well-thought-out IA can help prevent costly redesigns or re-architectures later in the development process. By investing time and effort into designing a solid IA upfront, businesses can avoid costly rework down the line.
Efficient Content Management: A structured IA can make it easier to manage and update content, reducing maintenance costs. When content is organized in a logical and efficient manner, it is easier to find, update, and maintain.
Scalability: A scalable IA can accommodate future growth and changes without requiring major overhauls. A well-designed IA should be flexible and adaptable, allowing businesses to easily add or remove content and features as needed.

Competitive Advantage
Differentiation: A superior IA can give a business a competitive advantage by providing a better user experience than its competitors. When a website or app is easy to navigate and use, it can stand out from the competition and attract more customers.
Increased Market Share: By attracting and retaining more customers, a well-designed IA can help a business increase its market share. A positive user experience can lead to increased customer loyalty and referrals, which can drive growth.
Good vs. Bad Information Architecture: Real-World Examples
Information Architecture Done Right
A Deeper Dive into Information Architecture Best Practices
Netflix IA
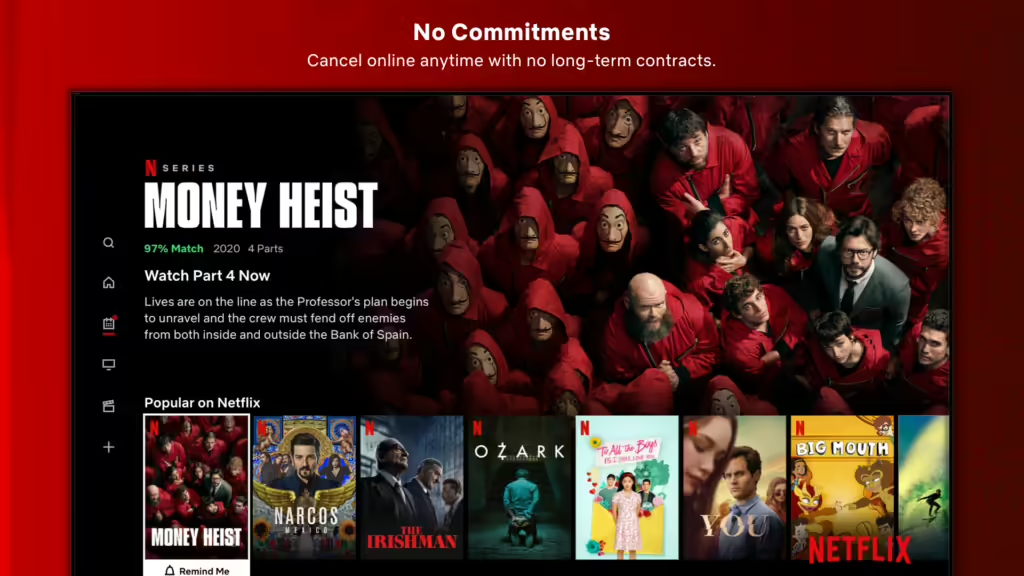
Intuitive Search: The search function allows users to search by title, actor, director, or genre.
Clear Categorization: Netflix organizes its content into genres, subgenres, and personalized recommendations. This makes it easy for users to find what they’re looking for.
Personalized Recommendations: Netflix uses algorithms to suggest movies and TV shows based on the user’s viewing history.
Amazon IA
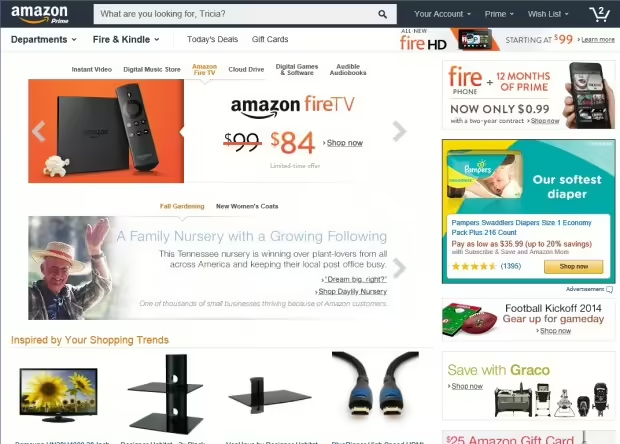
Faceted Navigation: Amazon’s product pages allow users to filter products based on various criteria like price, brand, color, and size.
Related Products: Amazon suggests related or complementary products based on the user’s current selection.
Customer Reviews and Ratings: Amazon displays customer reviews and ratings for each product, helping users make informed decisions
Google Search IA

Relevant Search Results: Google’s search algorithm delivers highly relevant search results based on the user’s query.
Auto-Complete: Google suggests possible search terms as the user types, saving time and effort.
Knowledge Graph: Google provides additional information about search results, such as images, definitions, and related topics.
Information Architecture Gone Wrong
A Website with a Cluttered Homepage
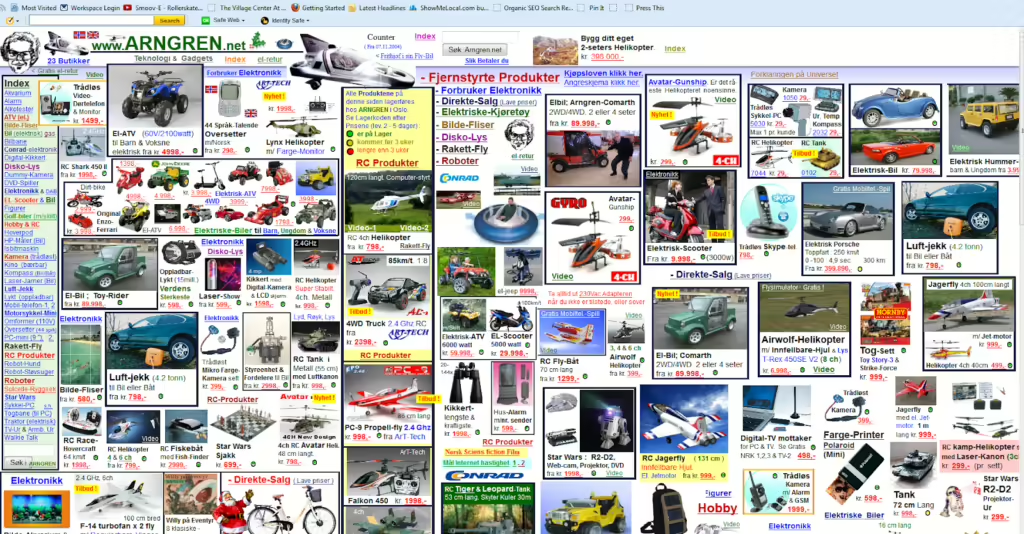
Too Much Information: A homepage with too many elements and information can be overwhelming for users.
Lack of Focus: A cluttered homepage can make it difficult for users to understand the website’s purpose or find what they’re looking for.
A Mobile App with Inefficient Navigation
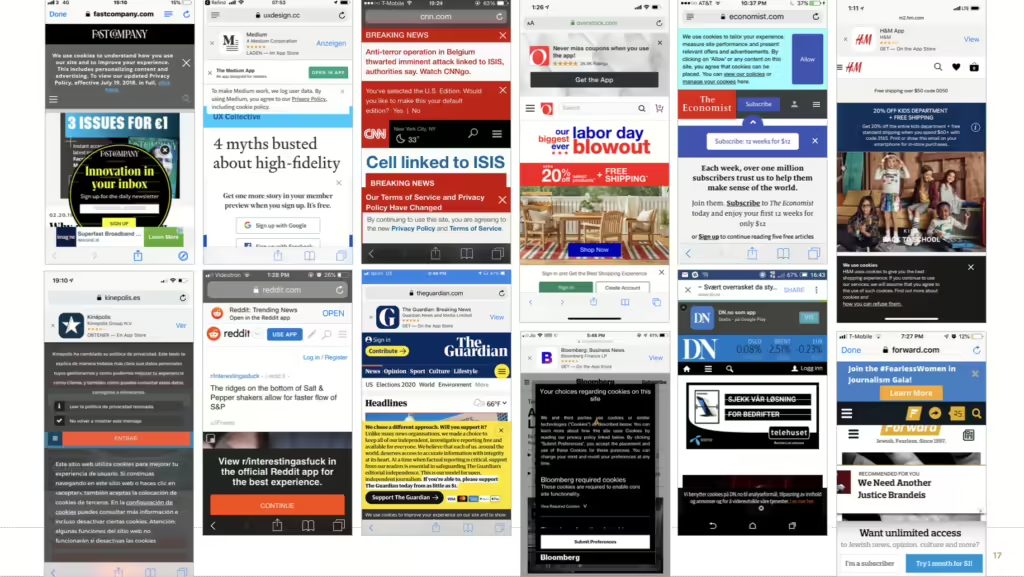
Hidden Menus: Menus that are difficult to find or access can frustrate users.
Complex Gestures: Requiring users to perform complex gestures to navigate the app can be confusing and time-consuming.
These examples illustrate the importance of well-designed information architecture. By providing a clear, intuitive, and efficient user experience, businesses can increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.

Information Architecture Design
Site Map: Create a site map to visualize the structure of your website or app. This will help you organize content and ensure that all pages are accessible.
Wireframing: Use wireframes to create low-fidelity mockups of your information architecture. This will help you visualize how the content will be organized and presented.
Prototyping: Create interactive prototypes to test your information architecture with users. This will help you identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Usability Testing
Card Sorting: Use card sorting to understand how users categorize information. This can help you organize your content in a way that makes sense to your audience.
Tree Testing: Use tree testing to evaluate the effectiveness of your site structure. This will help you identify any navigation issues.
Usability Testing: Conduct usability testing to observe users as they interact with your website or app. This will help you identify any pain points or areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement:
Analytics: Use analytics to track user behavior and identify areas for improvement.
Feedback Loops: Implement feedback loops to gather user feedback and make necessary adjustments.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your information architecture to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Additional Tips:
Keep it Simple: Avoid creating a complex information architecture that is difficult to navigate.
Use Consistent Labeling: Use clear and consistent labels for navigation elements, headings, and content.
Prioritize Content: Determine the most important content and make it easily accessible.
Consider Search Functionality: Implement a robust search feature to allow users to quickly find specific information.
Accessibility: Ensure that your information architecture is accessible to users with disabilities.
Mobile-First Design: Design your information architecture with mobile users in mind.
A/B Testing: Experiment with different IA approaches to determine what works best for your users.
Regular Updates: Keep your information architecture up-to-date to reflect changes in your business or user needs.
A Deeper Dive into Business Involvement in Information Architecture
Information architecture is a critical component of any digital product or service. It directly impacts user experience, search engine optimization (SEO), and overall business success. Therefore, it’s essential for businesses to be actively involved in the IA process.
Setting Clear Goals and Objectives:
Align IA with Business Strategy: Ensure that the IA aligns with the overall business strategy and objectives. For example, if the goal is to increase online sales, the IA should focus on making it easy for users to find and purchase products.
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish measurable KPIs to track the success of the IA. This could include metrics like conversion rates, bounce rates, and time on site.
Providing Subject Matter Expertise:
Domain Knowledge: Share your expertise on the business’s products, services, and industry. This will help the design team create an IA that accurately reflects the business’s unique needs.
Target Audience Insights: Provide insights into the target audience’s preferences, behaviors, and pain points. This will help the design team tailor the IA to meet their specific needs.
Reviewing and Providing Feedback:
SiteMaps and Wireframes: Review the sitemap and wireframes to ensure that they accurately represent the business’s structure and content.
Prototypes: Test prototypes to identify any usability issues or areas for improvement.
Content Strategy: Review the content strategy to ensure that it aligns with the business objectives and target audience.
Ensuring Alignment with Branding:
Visual Identity: Ensure that the IA is consistent with the business’s visual identity, including branding guidelines, color schemes, and typography.
Messaging: Ensure that the IA supports the business’s messaging and brand values.
Benefits of Business Involvement

Improved User Experience: A well-designed IA can lead to a more intuitive and satisfying user experience, which can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced SEO: A well-structured IA can improve a website’s search engine rankings, driving more organic traffic.
Reduced Development Costs: By getting involved early, businesses can help prevent costly mistakes and rework later in the development process.
Faster Time to Market: A well-defined IA can accelerate the development process, allowing businesses to bring their products or services to market more quickly.
By actively participating in the information architecture process, businesses can ensure that their digital products are aligned with their goals, meet the needs of their target audience, and provide a positive user experience.

